This month Hatch introduces a new kind of article, one that profiles a unique architecture for Android hardware. Overtime, as we showcase more unique hardware, you may find something which serves as a better platform to test your software than a generic Android tablet.
When Hatch first started making custom Android products around 2015 most demand revolved around mainstream retail tablet and smartphone devices. As visionaries imagined new use cases and industries created new demands, modified hardware architectures gained in popularity. One of the earliest high volume use cases that evolved from a niche are point of sale (POS) devices. Now there are several engineering and manufacturing companies that exclusively focus on this category since the global demand justifies a high level of support. Same thing is true for Rugged Android tablets and phones, however the high prices of these may still justify going custom if order volume is high enough.

Modifying hardware for a specific use case is only part of what’s needed to deliver an end product. The other, and arguably more important, part is designing the software to go with the hardware. Software entails a front end app and, usually, a back end system that interacts with the app. Once stable hardware is developed for industrial or business applications it stays the same for years, however elements of the software are regularly updated to improve user experience or resolve bugs.
Hatch sees the growing popularity of niche applications for Android as a good thing for the industry and synergistic with our business model. A new generation of niche Android products make it easier for entrepreneurs to realize their vision by running tests on existing hardware. Often existing hardware can be used for prototyping and beta testing. If testing goes well using existing hardware the next step is making custom Android hardware. Below we look at a device that’s been designed to replace the traditional keyless entry system.

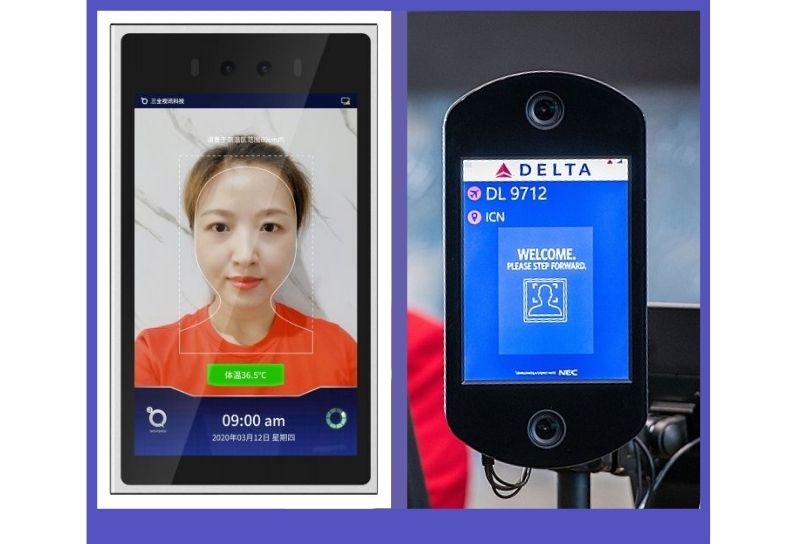
This Android device combines traditional systems with new technology. More powerful electronics supports new use cases, such as keyless entry using facial recognition. The facial database is stored in the device, either uploaded in a file or acquired using the camera, and recognition processing happens locally on the device in real time.
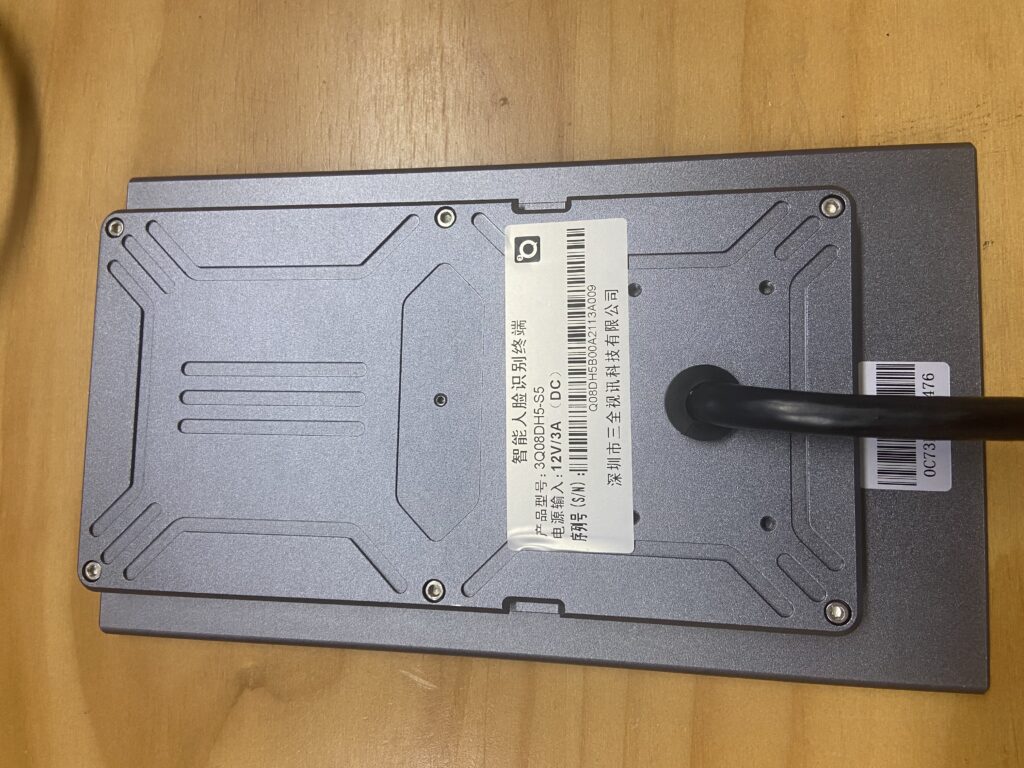

A Wiegand interface designed into the device’s motherboard connects to an external card reader. Wiegand is an older and still popular wiring protocol for connecting swipe card readers to an underlying access control system.
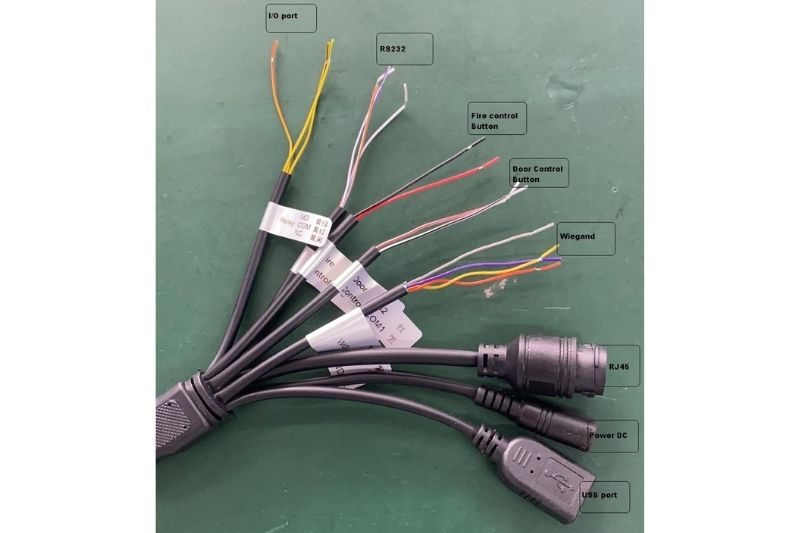
In addition to Wiegand there are several other interfaces including LAN (Ethernet), USB, RS-232, Power, and GPIO buttons. The RJ-45 Ethernet port can be used for PoE (power over Ethernet) or maintaining a hard-wired internet connection rather than relying on Wi-Fi. Other ports can be used for opening and closing access points mechanically or as defined by the user.
The IP65 case has been designed to withstand light rain and dust. This helps protect products exposed to rain or other outdoor conditions.
If the current architecture of the product detailed above serves your purpose better than a standard retail tablet we welcome you to use it for your initial prototype. Once you decide to make a custom version, future iterations of this product can add mobile data connectivity, body temperature sensing, or whatever customization serves your purpose best.

