Depending what your product is, where you are selling it and where/how it will be used you may be required to get Certificates for Electronics.
This article takes a closer look at a couple of the certificates for electronics and explains when and where they are needed and how to obtain the certificate.
The certificates we are taking a look at are:
- CE Certification
- FCC Certification
- ROHS Certification
- WEEE
What is CE?
The CE marking is a mandatory conformity marking for certain products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA) since 1985.
The CE marking certifies that the products have met EU health, safety and environmental requirements that ensure consumer and workplace safety
Manufacturers in the EU and abroad must affix the CE marking to those products covered by the “New Approach” directives in order to market their products in Europe. Once a product receives the CE marking, it can be marketed throughout the EU without having to undergo further product modification.
A CE marking does not indicate the quality of a product but rather its safety. It is also not an indicator of the origin of the products.
What regions require CE marking?
33 countries in total require the CE marking for certain products to go onto the market. The 28 member states of the EU plus EFTA countries (Iceland, Norway, and Liechtenstein) plus Switzerland and Turkey.
What products require CE marking?
The CE Marking Is Required Only for the Following Types of Products:
- Toys
- Machinery
- Electrical equipment
- Electronic equipment
- Personal protective equipment
- Pressure equipment
- Medical devices
- Active implantable medical devices
- In vitro diagnostics
- Radio and Telecommunications terminal equipment
- Simple pressure vessels
- Gas appliances
- Lifts
- Recreational craft
- Equipment and protective systems for use in explosive atmospheres
- Non-automatic weighing instruments
- Cableways
- Construction products
- Explosives for civil use
- New hot water boilers
- Measuring Equipment
Am I responsible for getting the CE certificate if importing from outside Europe?
Yes. When products are manufactured overseas (e.g. in China), it is the importer that is responsible to ensure the product has the correct certificate. Not all European importers are aware of this as most EU authorities, and their websites, tend to refer to the “manufacturer” as the party responsible to ensure CE compliance. However, when items are manufactured overseas, the importer is considered being the manufacturer. Thus, the responsibility to ensure ‘CE compliance’ cannot be shifted to a Chinese manufacturer.
How do I get the CE certificate?
Despite what many people believe, a manufacturer does not “get” the CE mark from a third party certification body or a European or national authority. The manufacturer affixes the CE marking in his own right and is allowed to do so when all requirements are fulfilled. A test or certification body may be involved in the process merely as a service provider. However, the body will not take over responsibility for CE compliance. Responsibility for CE compliance will always remain with the manufacturer (or private labeler).
Hatch, or other manufacturers, can work with these test or certification bodies to help you get the certificate for your device. At Hatch, we can also help you modify your product if you are having trouble achieving the certification standards.
It usually takes around 1 month for CE certification.
What are the risks/penalties for not having a CE?
EU customs can request CE certification documents to prove that the imported items are compliant with all applicable CE directives. If the importer cannot produce the requested documentation i.e. product certificates and technical documentation, the customs authorities will refuse the shipment to enter.
It has also happened that the authorities have come looking for certifications after the products have got through customs. If these certifications can’t be produced to prove compliance then the authorities can force a recall of all the products.
FCC – Federal Communications Commission
The FCC is an independent agency of the US government that was created by Congressional statute to regulate interstate communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable in all 50 states, the District of Columbia and U.S. territories.
The FCC label or FCC mark is a certification mark needed for electronic products that are manufactured or sold in the US. This mark indicates that the electromagnetic interference from the device is under the limits approved by the FCC.
What regions require the FCC Mark?
The US is the only region where this is required. However, the FCC mark is found even on products sold outside the US territory, because they are either products manufactured in the US and had been exported, or they are also sold in the US
What products require the FCC Mark?
FCC regulations apply to electronic products that may produce radio frequency pollution. There are 2 main types:
- Intentional Radiators
- Unintentional Radiators.
Intentional Radiator
This is a device that broadcasts radio energy (not infrared or ultrasonic energy) to perform its function. Intentional radiators are things like cell phones, CB radios, walkie-talkies, wireless connections, Bluetooth connections, and short-range broadcast equipment, wireless key-access systems. These devices intentionally use the radio spectrum and therefore always require FCC equipment authorization.
Unintentional Radiator
This is an electronic device that produces radio signals that are broadcast through space, or conducted along power lines. Devices that receive radio waves can also unintentionally radiate radio waves.
Unintentional radiators are very common everyday electronic devices such as television sets, computers, electronic games, digital cameras, and other devices with a chip/digital circuit in it.
The regulation in the USA defined per 47 CFR 15.3(k) defines an unintentional radiator as a device with electronics operating at over 9000 pulses per second (9 kHz) and using digital techniques. FCC regulations also apply to anything that connects to the telephone grid, such as phones, modems, faxes, etc.
How do I get FCC?
Unless you are fortunate enough to have an accredited in-house FCC laboratory in your company, the best choice is to involve an accredited third-party FCC lab at the design stage and then follow through with testing of your product at the lab.
Again a company like Hatch, or other manufacturers, can help you get this certificate. Like CE it will take around 1 month.
What are the risks/penalties for not having FCC?
It means you will be breaking the law. It is illegal to import, sell or lease covered equipment that has not undergone the required equipment authorization procedure.
The FCC has the power to seize goods, hand out fines and even jail sentences to offenders.
The person (or company) that sells the non-compliant digital device to the user has violated the FCC marketing rules as well as federal law and may be subject to an enforcement action by the Commission’s Field Operations Bureau that could result in one or more of the following:
- forfeiture of all non-compliant equipment
- $100,000/$200,000 criminal penalties for an individual/organization
- a criminal fine totaling twice the gross gain obtained from sales of the non-compliant equipment.
- an administrative fine totaling $10,000/day per violation.
You can see a list of previous enforcement actions taken here.
ROHS – Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive
“RoHS stands for Restriction of Hazardous Substances. RoHS, also known as Directive 2002/95/EC, originated in the European Union and restricts the use of six hazardous materials found in electrical and electronic products. All applicable products in the EU market after July 1, 2006, must pass RoHS compliance. RoHS impacts the entire electronics industry and many electrical products as well.”, www.rohsguide.com.
It is closely linked with the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive (WEEE) 2002/96/EC which sets collection, recycling and recovery targets for electrical goods and is part of a legislative initiative to solve the problem of huge amounts of toxic electronic waste.
What regions require the RoHS?
This directive was adopted by and is required in the European Union.
What materials are restricted?
It started with restrictions on 6 hazardous materials while an extra 4 (7-10 in the list) were added in March 2015.
Each European Union member state will adopt its own enforcement and implementation policies using the directive as a guide.
Here’s the list:
- Lead (Pb): < 1000 ppm
- Mercury (Hg): < 100 ppm
- Cadmium (Cd): < 100 ppm
- Hexavalent Chromium: (Cr VI) < 1000 ppm
- Polybrominated Biphenyls (PBB): < 1000 ppm
- Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDE): < 1000 ppm
- Bis(2-Ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP): < 1000 ppm
- Benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP): < 1000 ppm
- Dibutyl phthalate (DBP): < 1000 ppm
- Diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP): < 1000 ppm
*ppm = parts per million
What products are required to be ROHS compliant?
Basically most electronic products. Always assume that an electrical product is required to be RoHS compliant with importing to the European Union. As a matter of fact, the EU intends to introduce RoHS compliance as a certification requirement for all electronics by 2019.
How do I ensure RoHS compliance?
Luckily, there are many resources that can help a business ensure RoHS compliance. RoHS consultants help oversee compliance for businesses. These professionals ensure that all necessary parts and equipment are testing according to RoHS guidelines and that all testing is carefully documented.
Another option is laboratory testing. Companies can send their products to laboratories offering RoHS testing. The labs will test the company’s products and return the results and needed documentation. This takes around 1 to 2 weeks.
Another option is the use of handheld XRF analyzers. These small devices instantly test for the presence of elements and substances controlled by the RoHS Directive and offer instant results as well as saved results for RoHS documentation. Many businesses use a number of solutions to ensure full RoHS compliance.
What are the risks/penalties for not having ROHS?
Producers who place non-compliant products on the EU market risk facing severe penalties that include fines, impounded goods and the loss of the right to sell into the 25 EU Member States. Any country that can prove a product does not comply can levy fines against the vendor.
Each EU country sets its own fines which you can check here. For example, non-compliance with RoHS in Germany can result in a maximum fine of EUR 50,000.
There has already been clear evidence that failure to meet the RoHS Directive means lost sales:
- In 2006, Palm Inc.’s at the time extremely popular Treo 650 had to stop shipping to Europe as it did not meet RoHS requirements.
- Apple Computer Inc. products including the iSight Web camera, AirPort base station with modem, AirPort base station power-over-Ethernet and antenna, iPod Shuffle external battery pack and all versions of the eMac all-in-one desktop computer were withdrawn by the company for sale in the European market due to them not being compliant
The impact of RoHS is not limited to the EU; companies that supply components to customers who put products on the EU market must also be prepared to address RoHS or face the possibility of losing customers or even incurring liabilities.
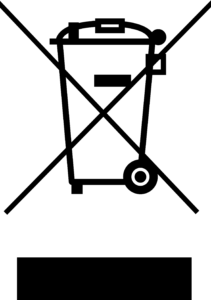
WEEE – Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Regulation (WEEE) is a directive in the European Union that designates safe and responsible collection, recycling and recovery procedures for all types of electronic waste.
Producers must register in every individual EU country. Without the WEEE registration, a product cannot be placed on the EU market.
- Producers will be expected to pay an annual registration fee to the appropriate Agency.
- Producers, or WEEE compliance schemes acting on their behalf, will be required to report data on the amount of EEE which they put onto the market.
- Producers will be required to report this data annually to the Agencies. It will be an offense not to do so.
What are the Categories of WEEE?
The WEEE directive sets a total of 10 categories of WEEE for reporting purposes.
- Large household appliances
- Small household appliances
- IT and telecommunications equipment
- Consumer equipment
- Lighting equipment
- Electrical and electronic tools
- Toys, leisure, and sports equipment
- Medical devices
- Monitoring and control instruments
- Automatic dispensers
How are ROHS and WEEE related?
WEEE compliance aims to encourage the design of electronic products with environmentally-safe recycling and recovery in mind. RoHS compliance dovetails into WEEE by reducing the number of hazardous chemicals used in electronics manufacture.
Put another way, RoHS regulates the hazardous substances used in electrical and electronic equipment, while WEEE regulates the disposal of this same equipment.
It’s never safe to assume that the product you are importing has the correct certifications, especially when dealing with some Chinese manufacturers. With a company like Hatch, we make sure we understand what certifications you need and we look after acquiring them for our clients.
These are just a couple of the main certifications required or directive that needs to be complied with for electrical products. If you would like to know more about these or any other certification let me know in the comment box below.
If there is any other topic you wish to know more about you can also let me know in the comment section.
Garry @ Hatch